Qvalon Blog article content
By: Jul Domingo
In 2010, Toyota had to recall 5.3M cars because of improper floor mat installation causing the accelerator pedal to get trapped.
It's a big loss, but one that could have been avoided by observing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Since consumer trust stems from offering high-quality and safe products, GMPs are necessary to ensure that companies comply with quality standards.
A business that follows Good Manufacturing Practices guidelines is more likely to improve consumer confidence and brand reputation. Otherwise, they might receive an FDA 483 warning letter for their violations and lose 41% of shoppers , who will readily abandon brands they don't trust.
GMPs ensure manufacturers avoid consumer incidents that may lead to distrust, bad reputation, criminal losses, and business falloff. In 2021 alone, FDA issued 2430 objectionable observations, of which 1751 letters are from the food industry alone.
Learn the basics of GMP to make sure your retail business is compliant.
What are Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)?
Good Manufacturing Practices help manufacturers minimize health and safety risks in the production and distribution of their products, and maintain a sanitary environment throughout the production cycle. It also ensures the products have undergone a thorough quality check from the first batch to the nth batch.
GMP prevents:
-
Harm to consumers
-
Contamination
-
Mixups
-
Errors
All the while, guaranteeing all processes, materials, and labor are in a sterile environment. GMPs cover a wide range of industries, such as:
-
Pharmaceutical products
-
Medical equipment
-
Food and Beverages
-
Cosmetics
-
Dietary supplements
-
Automobiles
-
Fashion Industry
GMP non-compliance can lead to license cancellations, product recalls, and prosecution. It happened to two doctors who were recently convicted due to illegal distribution of an unapproved “cancer treatment” drug in November 2021.

Difference between GMP and cGMP
cGMP stands for current Good Manufacturing Practices. The “C” is almost always overlooked, but it creates a difference. While GMP refers to the general requirements of FDA regulations, cGMP refers to the current controls and procedures and satisfies the continuous necessity to improve GMP with technology.
Here are the notable key differences between GMP and cGMP:
-
Cost. Since cGMP relies on the latest technology, it tends to be more expensive to maintain than GMP.
-
Accessibility. GMPs cover a wide range of applications while cGMPs are more specific and comprehensive.
-
Quality. Both GMP and cGMP are designed to produce high-quality and consistent results, but cGMP can be more effective from a security and reliability standpoint due to the resources required.
-
Scope. GMP applies to different business operations and procedures that demand quality while cGMP is usually limited to the actual process of manufacturing goods.
A good example is the cGMP modernization of the food chain industry, which calls for extensive control. FDA requires to monitor "time, temperature, humidity, aw, pH, pressure, flow rate, and manufacturing operations such as freezing, dehydration, heat processing, acidification, and refrigeration to ensure that mechanical breakdowns, time delays, temperature fluctuations, and other factors do not contribute to the decomposition or contamination of food.”
5 GMP principles
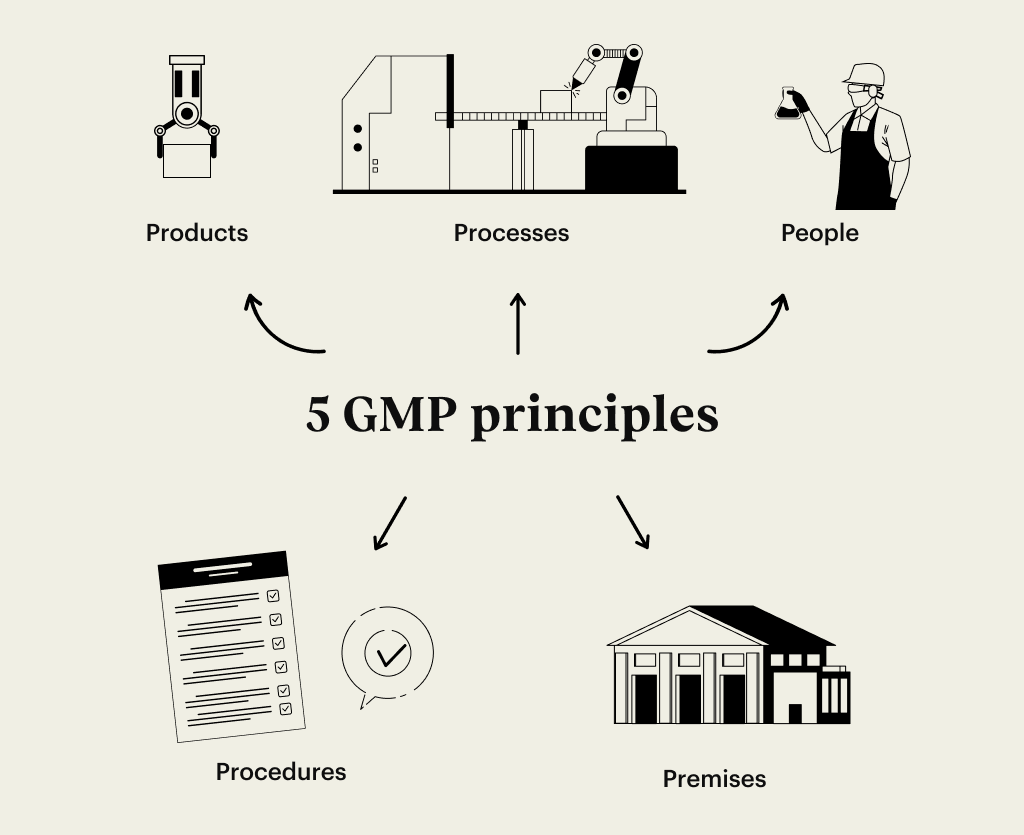
Focusing on the 5 GMP principles enables companies to comply with Good Manufacturing Practices. Let’s dive into them in more detail:
Products
Your products, from ingredients to packaging materials, should be protected from physical, chemical, and microbial contaminations. In other words, quality standards should be present during testing, production, and distribution.
If products are in non-compliance with GMP, they are tagged as "adulterated" under the law. FDA considers a product adulterated "...if it includes any filthy, putrid, or decomposed substance, or if it is prepared, packed, or held under unsanitary conditions."
Pharmaceutical manufacturers and distributors are good examples. The quality of each batch remains the same throughout the whole process—from the testing of ingredients to packaging and labeling of final products, they must constantly meet standards.
Processes
Process is at the heart of GMP, and includes sanitizing equipment, facilities, utensils, and stock area to prevent contamination and attain the desired quality of products. One example is Good Manufacturing Practices in the food industry, specifically the sanitation process to ensure the safety of all consumables.
Processes, above all, must be consistently documented, communicated, and evaluated. To streamline their documentation and real-time evaluation, companies should rely on management software. Employees can use the software to remind themselves of processes.
People
People aka personnel pertains to the management and all staff in the organization. Your staff needs to be properly oriented and knowledgeable about GMP compliance, especially regarding sanitation and hygiene.
Sick employees should not be allowed to work, in combination with precautions, such as wearing gloves, hairnets, and proper clothing, going without food, and not smoking.
You can't take a chance on the health of your staff or customers, given that a pandemic is still in full swing. FDA provided retail food stores with the best practices to safeguard workers and consumers during Covid-19. QVALON also comes with a pre-set of COVID-19 checklists.
Procedures
Procedures refer to a set of guidelines that all employees need to follow for consistent high-quality production. The same thing with processes, documentation of procedures is a Good Manufacturing Practices requirement. Employers must also observe if the actual practice has any deviation from the standard procedures. Regular internal inspection will prepare them for FDA surprise audits.
This principle is critical because once there's a defect or potentially unsafe output in a batch, you won't have to inspect the entire production. With proper documentation of procedures, the staff can easily point out the source of the problem and address the matter right away.
Establish consistent procedures regardless of who is on duty by instructing retail employees to check and document the quality of the products upon receipt. Once the final products are ready for distribution to retail shops, there must be a quality check before their dispatch.
Premises
The premises serve as the base of all other GMP principles. To further ensure the sanitation and safety of the products, the premises should be clean all the time. The main facilities should be far from any external risks such as flooding, pollution, infestations, and waste buildup.
Restaurants and food manufacturers, for example, can accumulate too much food waste. The premises must consider the place for waste storage. Meanwhile, the equipment and utensils must be thoroughly cleaned and maintained at all times.
The layout, ventilation, and water supply of the place should always be in a favorable condition. With the accessibility of supplies, cleaning and maintenance will be easier. Staff should also have adequate facilities and tools to maintain personal hygiene.
GMP Regulations
Good Manufacturing Practices have no global standard regulation. The regulations depend on the national government where the business is located. Each country has its respective law to ensure the public consumption of hazard-free quality products.
As already mentioned for the United States, the governing body is the Food and Drug Administration. FDA implemented GMPs under the Code of Federal Regulations Title 21 with respect to the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act). Each industry has its particular GMPs stated in the regulations.
FDA is also responsible for inspection and the call for criminal prosecution in the case of non-compliance. GlaxoSmithKline, for instance, faced both criminal and civil charges amounting to $3 billion. The reasons are due to failure to disclose safety data, bribed physicians, false statements, and reported false best prices.
GMP Standards
GMP regulations are the list of detailed instructions on the enforcement of GMP. GMP standards, on the other hand, are the criteria and specifications to ensure the quality and safety of products.
Complying with these standards will lessen the stoppage of operation due to product recalls and seizures. Here are four courses of action you can take to meet the GMP standards:
Compliance Training
People is one of the 5Ps of GMP principles. And it's the company's responsibility to educate these people about the right practices when it comes to operation. Compliance training will allow them to have a better understanding of their duties to meet the GMP requirements. It will polish the operation while reducing the risk of committing violations.
The training you can provide may relate to sanitation, maintenance, recordkeeping, and other relevant Standard Operating Procedures. For food and beverages companies, FDA mandated the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA). This training is a U.S food safety law including topics like product and facility plans, risk assessment, and preventive controls.
Quality team
A quality team is like a set of internal auditors who regularly test the quality control of production. First, you have to make sure that they are knowledgeable enough to ensure GMP compliance. Equip them to conduct monthly or quarterly inspections. These regular inspections will help identify what aspects of operation need improvement.
With a quality team of your own, you’re more prepared for unexpected FDA observations. Hence, you may avoid possible GMP non-compliance. The quality team members must know their specific contributions. Say they are food chain employees. Other members may focus on observing food quality and preparing reports about it. While others can be selected to investigate customer complaints.
Validation
Validation explains the processes, tests, activities, methods, and equipment needed to achieve consistent and quality products in a documented form. It includes the complete and well-tested manufacturing process. The testing can be prospective, retrospective, and concurrent for the production and distribution of the products.
Its purpose is to ensure that before implementing a certain process or system, the validation test already proved its effectiveness. To preserve food, for example, it has to go through the food irradiation process. The computer system validation will ensure that the system can meet the desired result without any harmful effects.
Below are the four types of Good Manufacturing Practices validation:
-
Process validation. FDA listed the process validation requirements in Section 820.75 of the Quality System Regulation (QSR). It includes a high degree of assurance for installation, design, performance, and operation.
-
Cleaning and sanitation validation. The purpose of this validation is to reduce the probability of cross-contamination between products, especially for pharmaceutical companies.
-
Computer system validation. Also known as software validation. It involves formal testing to prove that the software satisfies its requirements to avoid programming issues.
-
Analytical method validation. Its purpose is to validate methods and verify that they meet requirements for the intended use. Verifying methods are critical before applying them to analytical test samples.
Surprise Audits
In contrast to the assessment of the quality team, actual internal auditors conduct surprise audits. In fact, the manufacturer can select and train a GMP auditor among them. Or in some cases, even the employers themselves can do a GMP audit. To ensure effectiveness, it's important to consider previous inspections. Review the past recommendations taken and consider external auditors' feedback. Self-inspections at regular intervals will eliminate the risks of GMP non-compliance.
Here are some areas you need to include in your audit checklist:
-
Staff performance and compliance
-
Warehouse cleanliness and organization
-
Quality of sanitary operations
-
Availability of sanitary facilities
-
Equipment and utensils maintenance
-
Effectivity of processes and controls
-
Storage and distribution procedures
-
Deficiency in internal control
GMP manual and its basic concepts
The key to creating a successful manufacturing process is to understand all the basic concepts first. Below are the fundamental concepts of Good Manufacturing Practices:
Quality management
Quality management ensures that all operations follow the GMP guidelines. For quality management systems, ISO 9001:2015 provides a comprehensive list of requirements. QMS is mandatory for some companies, in particular if they seek GMP certification. Compliance with the ISO standards is proof of a company's ability to consistently produce high-quality products concerning the regulatory requirements including GMP.
Building and structures/premises
Manufacturing is carried out in buildings and structures. Size, location, design, and construction are vital to prevent cross-contamination. Additionally, these factors contribute to the efficiency of cleaning and maintenance. Last point of concern is to consider how your location affects the environment. We’ve all heard horror stories about factories poisoning the water around their facilities. As much as possible, account for possible chemical and air pollution, and try to keep your operation away from surrounding areas.
Raw materials
GMP strictly prohibits unpacking and removing raw materials from storage for unauthorized personnel. Each lot of raw materials needs to be tested before usage, and proper documentation, storage, and management must be in place at all times. FYI: Raw materials hazard risks are highest for drugs, food, and beverages.
Equipment
Equipment has a direct impact on product quality, so your staff must maintain it properly. Its qualification includes proper installation, operation, and performance. If you own a restaurant, schedule regular cleaning and maintenance of commercial range burners, and track and document the date of maintenance.
Sanitation and hygiene
Sanitation and hygiene require the constant cleanliness of everyone on the manufacturing site. This reduces sources and types of contamination. Cleanliness procedures for equipment and facilities are also part of Good Manufacturing Practices. Staff members must wear their appropriate clothing and attire, including face masks if necessary. Moreover, it is the company's duty to provide them with all the amenities they need to ensure high-level sanitation.
Staff
This GMP principle requires proper education, training, and experience for all staff. The company should also maintain an adequate number of employees in every site to avoid overcrowding which leads to higher contamination risk. The ideal standard is GMP training for all employees. FDA requires food chain companies to train under FSMA as mentioned earlier.
Validation and qualification
Qualification is the act of providing documented evidence that the specific facility, equipment, or system is ready for the intended use. Validation demonstrates in a documented form how the processes, tests, methods, etc. can produce the desired quality product. Both qualification and validation need to submit proper documentation for design qualification (DQ), installation qualification (IQ), and operational qualification (OQ).
Quality inspections and audits
As discussed, inspections and audits observe the implemented systems, procedures, and controls. The audit results should be documented and analyzed to understand the loopholes in the operation. At regular intervals, it can help increase quality control and reduce future failures. Employers or audit teams must check all areas of operation from the warehouse, manufacturing plant, admin offices, and retail stores. This will give them an overview of the entire production cycle and how it performs with respect to GMP.
Documentation and record keeping
All procedures taken to achieve the high-quality finished product must be recorded. Upon the receipt of raw materials to production to actual selling, the company needs to log everything. GMP requires the use of Good Documentation Processes (GDP) which are a part of quality management system requirements. The records must document all GMP activities with proper review and approval. GDP entails that documents must be:
-
Permanent
-
Concise
-
Clear
-
Legible
-
Accurate
-
Timely
-
Complete
Complaints
Complaints are an essential aspect of GMP because it gives a negative external perspective. If there's a complaint, it only means the product is defective or poor in quality. With an effective complaint system, managers can quickly address matters and provide solutions. The earlier you settle customer complaints, the more you can save money from defective outputs. In the case of Toyota, those 5.8M car recalls could have been avoided had complaints been communicated earlier.
Compliance with GMP rules
To assure GMP compliance, you need to know the specific GMP regulations in your country first. Invest time and resources in studying the complexities of the rules. From there, start observing the current operation and list down the areas that fall short of the requirements.
Below are more steps to sustain compliance with GMP rules:
-
Don't let an employee work in the manufacturing plant without proper training.
-
Establish and invest in your quality team so they can effectively conduct regular assessments.
-
Implement improvement measures based on the assessment and audit reports.
-
Focus on the validation activities mentioned above so you won't miss the basic GMP requirements.
-
In addition to the quality team assessments, conduct surprise audits to double-check previous findings.
-
Random observation of the operation to see the actual day-to-day performance.
QVALON helps you adhere to GMP rules
Save yourself the worry of receiving a warning letter from the government by using automation technology. With QVALON, you follow GMP more efficiently using these tools:
Inspections and audits
After an audit, expect an instant checklist and a list of templates for monitoring and evaluating processes in compliance with GMP. Each inspection results in the assignment of tasks to staff.
Collaboration
Upon inspection, automatically assign the appropriate actions among your staff without delay. This tool will let you reach them via voice and video call. With our Video Consulting feature, you can virtually observe the site anytime.
Task Management
Avoid delays in reporting and distributing work by automating task management. Schedule ahead and receive feedback in real-time. Avoid the omission of any GMP requirements with deadline alerts.
Learn more about how we can help your retail business here.